When we study the transmission system of four or Multi-axle vehicles, we get familiar with very phrases like gearbox, clutch, propeller shaft, drive axle, differential etc. An engine produces power. And the clutch transfers power to the gearbox which comes produces from the engine, and the gearbox transfers the power to the drive axle. Finally, the drive axle provides motions to the driving wheel, which may be a rear wheel, front or all-wheel. It completely depends on the type of driving system in a vehicle. Before power transmits into the drive axle, it passes through the differential. So, in this post we will know that, What is a differential? And How it works? What is the meaning of differential? Types of differential in automobiles and etc.
Page Contents
What is Differential?
The Differential is a mechanism that differentiates the power transmission ratio to the wheels. It is generally used in vehicles to enable a smooth and efficient turn. The differential is located on a powered axle. The final drive is also integrated with differential. The Final drive is the last stage in power transmission from the engine to the powered wheel. It reduces the gearbox’s output shaft speed for harmonizing with the powered wheels.
As you can see below in the image, the differential gear hub is located in the rear axle. Where this is a rear-drive axle vehicle’s layout.
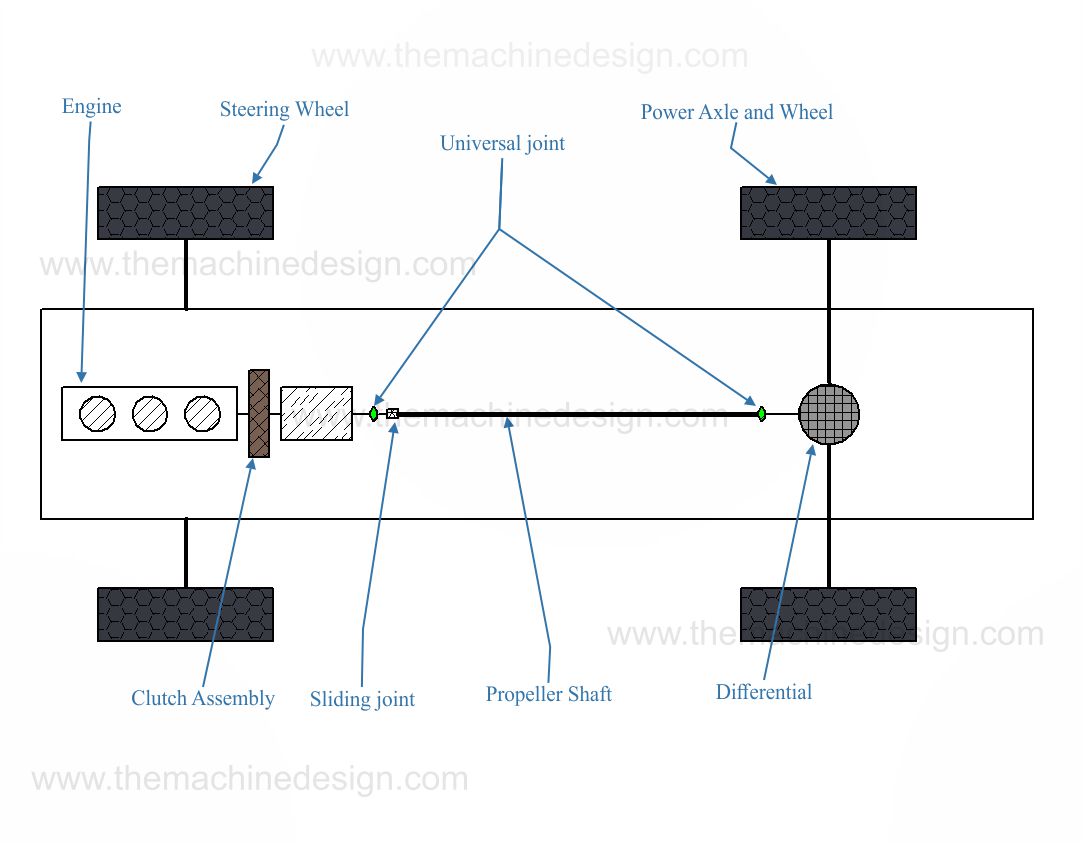
Basically, the differential gear consists of three shafts. One shaft is the power input shaft, which is connected to the propeller shaft. Another two shafts are the output shafts, which transfer motion to the powered wheel. These shafts are connected with the bevel gears assembly in the housing. The differential allows higher rpm to the outside wheel and reduces the inside wheel’s speed during turning the vehicle.
Without a differential, taking a quick turn at a higher speed is impossible.
Also Read:
- Sustainable Office Furniture
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Cars: A Closer Look at the Technology
- Which metal is been used to make Cybertruck’s robust skin?
Construction of Differential:

As shown in the above image, there are various parts in this differential unit. This is an open differential. A pinion gear is mounted on the pinion shaft. Actually, this pinion shaft is a propeller shaft. This pinion gear rotates the big ring gear. A Carrier unit is mounted on the ring gear. It consists of two bevel pinions (planet pinions) and two bevels (sun) gears. The sun bevel gears are connected with the half shaft of the rear axle. A differential housing covers this whole assembly. And axle housing covers the half shaft.
Working of Differential:
What happens in the differential case when the vehicle moves straight?
When a vehicle moves on a straight path, the differential gear assembly (whole assembly) turns as a unit. The ring gear, both differential side gears and both axles are in this unit. The two planet pinions do not rotate with the pinion shaft. Because they apply the same force on the sun pinions. Therefore, both sun pinions rotate at the same rpm with the ring gear.

What happens in the differential case when the vehicle turns right?
During the right turn, the vehicle’s right (inside) wheel rotates slower than the left (outside) wheel. Inside of the differential case, the planet pinion rotates on its self-axis along with the ring gear. This allows the independent rotation of both side wheels. As the carrier rotates with the ring gear, the planet pinion rotates at the same rpm. But, due to the pinion’s spinning on the self-axis, it reduces the rpm of the right sun gear and increases the rpm of the left sun gear. The vice-versa action happens while the vehicle turns left. the plane pinion reduces the rpm of the left side sun gear and increases the right side sun ears rpm. For a better understanding please go through this video.
Other uses of Differential:
The differential gear helps during turning and cornering at a continuous speed. It’s also having other uses. Like,
- It transfers power at 90° with independent rpm when required.
- Reduces the pinions rpm at the ring gear. As a result, reduced rpm and higher torque at wheel.
Types of Differentials:
Types of differential in automobiles are:
- Open or Conventional differential (we have studied in this post).
- Limited Slip Differential (LSD).
- Locking Differential.
- Torque Vectoring differential

Differential Case
courtesy – American Axle & Manufacturing, Inc.

courtesy – American Axle & Manufacturing, Inc.
Also Read:




The business model of car that you have shared is something new to read today. Thanks for the information on this topic. Subscribed your blog.
The information about the gear and the differences is really good to know. Thanks for the valuable information on this topic. Subscribed your blog.